Home > Products > intermediate
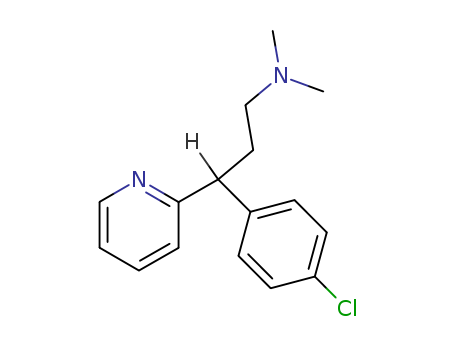







CasNo: 132-22-9
MF: C16H19 Cl N2
|
Environmental Fate |
Toxicity of antihistamines is usually related to their anticholinergic effects and may include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, and other GI effects, as well as dizziness, tinnitus, lassitude, incoordination, fatigue, blurred vision, diplopia, euphoria, nervousness, insomnia, and tremors. Acetylcholine is competitively blocked at muscarinic receptors, resulting in symptoms of anticholinergic poisoning. Concurrent use of alcohol, tricyclic antidepressants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants along with antihistamines may exaggerate and extend the anticholinergic and CNS depressant effects of antihistamines; concurrent use is not recommended. Products that were marketed prior to the FDA safety alert but not approved by the FDA included multisymptom cold medications comprised of drug combinations of chlorpheniramine with decongestants, antitussives, and analgesics. Risks associated with the use of these products included improper use in children and infants, potentially risky combination of ingredients, and patients receiving too much or too little medication because of problems with the way some ‘extendedrelease’ products were made. Newborn and premature infants are even more prone to anticholinergic side effects and an increased susceptibility toward convulsions; thus, this drug is not recommended at all in this age group. Geriatric patients are also more prone to anticholinergic effects, and a paradoxical reaction characterized by hyperexcitability may occur in some children taking antihistamines. Overdosage may also produce central excitation resulting in convulsions. |
InChI:InChI=1/C16H19ClN2/c1-19(2)11-9-16(14-4-3-10-18-12-14)13-5-7-15(17)8-6-13/h3-8,10,12,16H,9,11H2,1-2H3
-
Here we report the design of an enzyme-i...
The invention belongs to the field of me...
The alkylation of amines by alcohols has...
3-Aryl-3-(2-pyridyl)propanals 3, useful ...
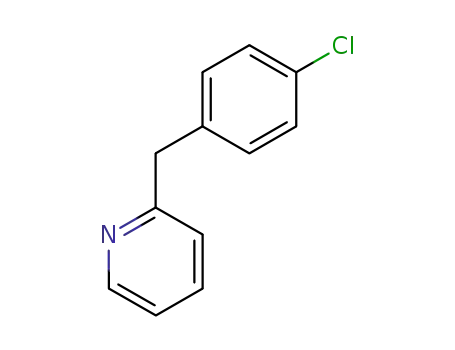
2-(4-chlorobenzyl)pyridine
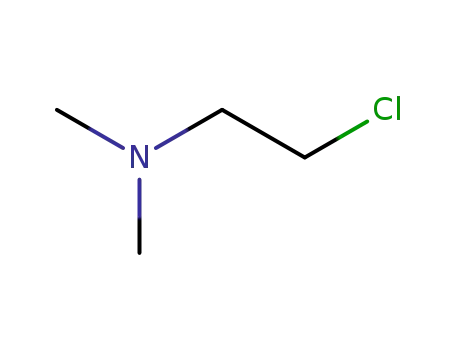
2-(dimethylamino)ethyl chloride

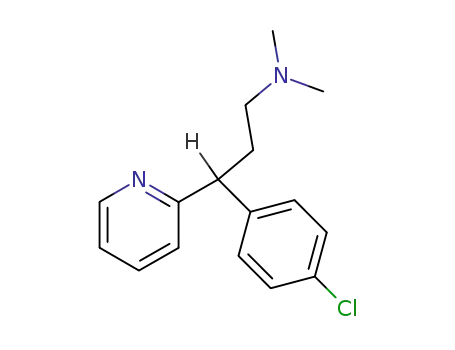
Chlorpheniramine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
potassium amide;
|
|
|
With
sodium amide;
|
|
|
2-(4-chlorobenzyl)pyridine;
With
sodium amide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 - 25 ℃;
for 1h;
2-(dimethylamino)ethyl chloride;
In
tetrahydrofuran; toluene;
at 30 - 45 ℃;
for 2h;
|
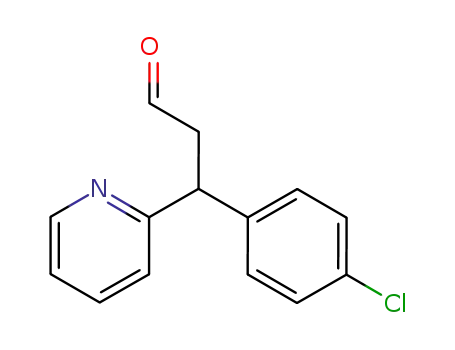
3-(p-chlorophenyl)-3-(2-pyridyl)propanal

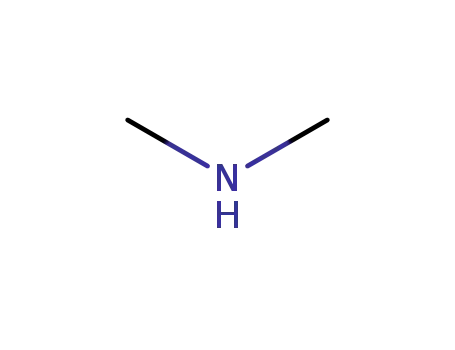
dimethyl amine


Chlorpheniramine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogen;
platinum(IV) oxide;
In
toluene;
at 120 ℃;
for 12h;
under 38000 Torr;
|
100% |
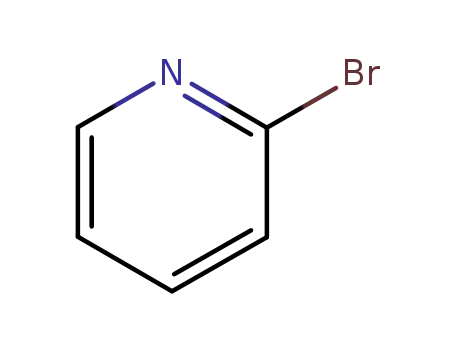
2-bromo-pyridine
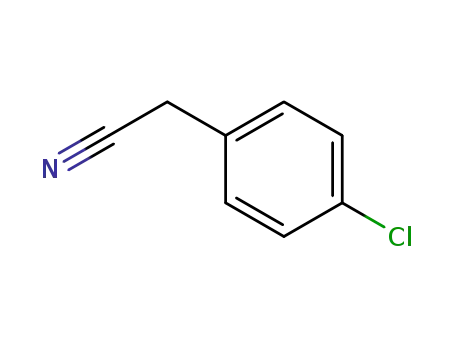
p-chlorobenzyl cyanide
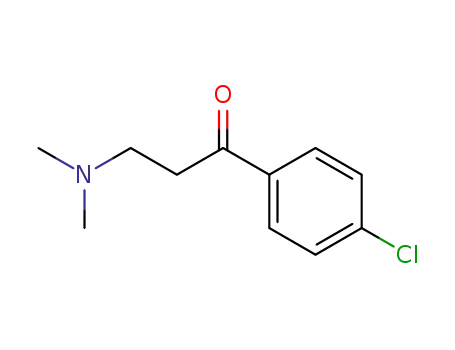
1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-dimethylamino-1-propanone
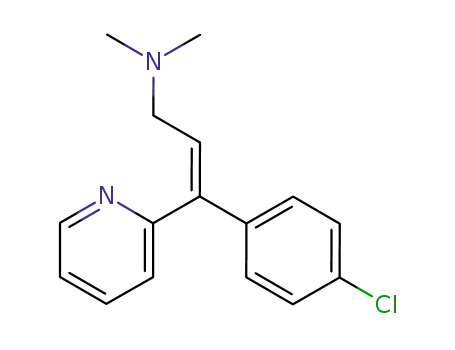
1t-(4-chloro-phenyl)-3-dimethylamino-1c-[2]pyridyl-propene
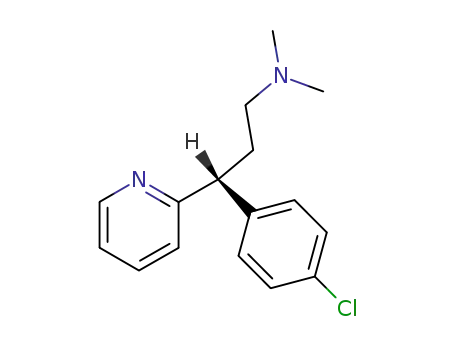
L-chlorpheniramine
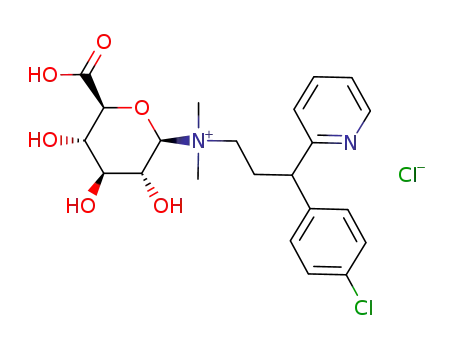
((2R,3R,4S,5S,6S)-6-Carboxy-3,4,5-trihydroxy-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yl)-[3-(4-chloro-phenyl)-3-pyridin-2-yl-propyl]-dimethyl-ammonium; chloride
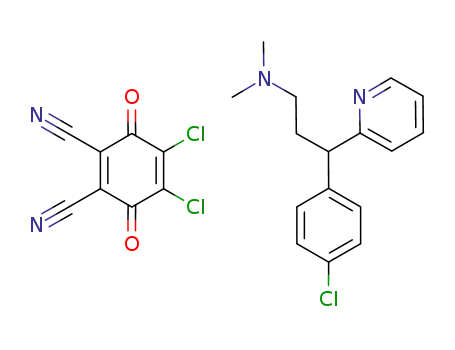
C8Cl2N2O2*C16H19ClN2
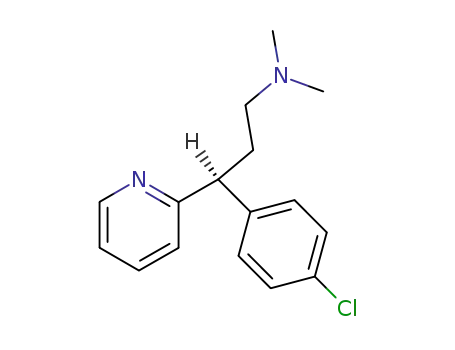
dexchlorpheniramine