Home > Products > intermediate
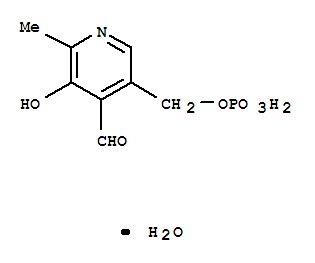







CasNo: 41468-25-1
MF: C8H12NO7P
Appearance: pale yellowish white crystalline powder
|
Application |
Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP), an active form of vitamin B6/ pyridoxine is the coenzyme of amino acid metabolism.Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate monohydrate has been used:as a component in the reaction mixture for ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) activity assayas a standard to quantify the concentration of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of childrenas a dietary supplement to study its effects on the lethal phenotype of mutant flies. |
|
General Description |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP, vitamin B6) is an essential cofactor in all living systems. It is one of the most versatile cofactors and participates in transamination, decarboxylation, racemization, Cα-Cβ cleavage and α-β elimination reactions. PLP plays an important role in amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism and has been implicated in singlet oxygen resistance. PLP can be used as a dietary supplement in cases of vitamin B6 deficiency. Reduced levels of PLP in the brain can cause neurological dysfunction. By inhibiting AGE formation and working as a coenzyme in chemical reactions, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate can support healthy nerve, eye, cardiovascular and kidney function. |
|
Biological Activity |
Pyridoxine participates in the production of lipid and neurotransmitters. Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP) serves as a cofactor to stabilize carbanions at Cα of amino acids. Pyridoxine deficiency results in peripheral neuropathy. Absence of PLP leads to neonatal epileptic encephalopathy. PLP acts as a coenzyme in transamination, decarboxylation and deamination reactions such as the conversion of dopa into dopamine; of glutamate into γ aminobutyric acid (GABA); of histidine to histamine. PLP works mechanistically through formation of a Schiff-base. |
InChI:InChI:1S/C8H10NO6P.H2O/c1-5-8(11)7(3-10)6(2-9-5)4-15-16(12,13)14;/h2-3,11H,4H2,1H3,(H2,12,13,14);1H2