Home > Products > intermediate
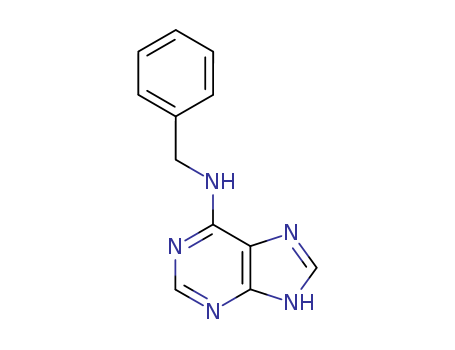







CasNo: 1214-39-7
MF: C12H11N5
Appearance: white to light yellow crystalline powder
|
Preparation |
synthesis of 6-benzylaminopurine: To 5g hypoxanthine, add 20mL SOCl2, 0.25g DMAP, 10gBTC dissolved in 20mL SOCl2. Heat and add BTC/SOCl2 dropwise. Reflux (refrigerant cooling) to complete dissolution, steam out SOCl2 (containing phosgene, which is used for recovery), evaporated (drained), cooled to room temperature to obtain a milky yellow solid (6-chloropurine and DMAP.Hcl). Directly add 4g benzylamine and 25g triethylamine to it, heat to 70~80 ℃, or microwave heating, until the 6-chloropurine reaction is complete (TLC monitoring), add ethanol, the solid filtered out is washed with ethanol, and dried to obtain 7 g of product 6-benzylaminopurine with a brown color.Preparation and biological activity of 6-benzylaminopurine derivatives in plants and human cancer cells |
|
Health Hazard |
6-benzylaminopurine (6-BA) is widely used in agriculture and horticulture as plant growth regulator. Its excessive use may pose a potential risk to both environment and human health, which is causing great concern. Vapor is irritating when breathed at high concentrations. Contact with liquid causes irritation of skin and burning of eyes; Vapors cause a slight smarting of the eyes or respiratory system if present in high concentrations; If spilled on clothing and allowed to remain, may cause smarting and reddening of the skin. |
|
Trade name |
ABG? 3034; ACCEL?; AGTROL?; 6-BA?; BA? (growth stimulant); CHRYSAL BVB?; EXILIS?; PERLAN?; PROMALIN?; SD? 4901; SQ? 4609 |
|
Safety Profile |
Moderately toxic by ingestion andskin contact. Human mutation data reported. Whenheated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx. |
|
Potential Exposure |
A polyamine plant growth regulator used to lengthen and enhance the shape of apples and to increase the fruit set in pears. It increases the yield of pistachios and tomatoes. Not listed for use in the EU countries. |
|
Shipping |
UN3259 Amines, solid, corrosive, n.o.s, or Polyamines, solid, corrosive, n.o.s., Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8—Corrosive material, Technical Name Required. |
|
Purification Methods |
It is purified by recrystallisation from aqueous EtOH. It has at 207 and 270nm (H2O), 268 nm max (pH 6), 274nm (0.1 N HCl) and 275nm (0.1 N NaOH). [Daly J Org Chem 21 1553 1956, Bullock et al. J Am Chem Soc 78 3693 1956, Beilstein 26 III/IV 3575.] |
|
Incompatibilities |
May react with strong oxidizers such as chlorates, peroxides, nitrates, etc. May release heat on contact with water. Solid and corrosive amines are chemical bases. Neutralize acids to form salts plus water in exothermic reactions. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. May generate flammable gaseous hydrogen in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. |
|
Waste Disposal |
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed. |
|
Application |
6-Benzylaminopurine solution has been used as a component in the Murashige & Skoog medium (MS) for culturing mandarin explants and plantlets of Dendrocalamus asper (Schultes f.). It has also been used as a supplement in Nitsch and Nitsch medium (NN) of grapevine explants. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: 6-Benzylaminopurine is a member of the class of 6-aminopurines that is adenine in which one of the hydrogens of the amino group is replaced by a benzyl group. It has a role as a plant metabolite and a cytokinin. It derives from an adenine. |
|
General Description |
6-Benzylaminopurine is a plant growth regulator that belongs to the class of first generation synthetic cytokinin used in agriculture commodities. |
|
Agricultural Uses |
6-Benzylaminopurine is a plant growth promoter, is the first applied synthetic cytokinin, mainlyused as a broad- spectrum plant growth regulator. It can be used inagriculture, horticulture, for plants at different stages, from germination to harvest. It enhance the shape of apples and to increase the fruit set in pears. It increases the yield of pistachios and tomatoes. Not listed for use in EU countries. Registered for use in the U.S. |
InChI:InChI=1/C12H11N5/c1-2-4-9(5-3-1)6-13-11-10-12(15-7-14-10)17-8-16-11/h1-5,7-8,10H,6H2,(H,13,14,15,16,17)
In the course of our study on fungal pur...
The structure-based design, synthesis, a...
N6-isopentenyladenosine is an anti-proli...
-
The mechanism of formation of N2-benzylg...
-
Abstract: The features of reactions of a...
The chlorination of hydroxy aza-arenes w...
Nucleoside phosphorylases are involved i...
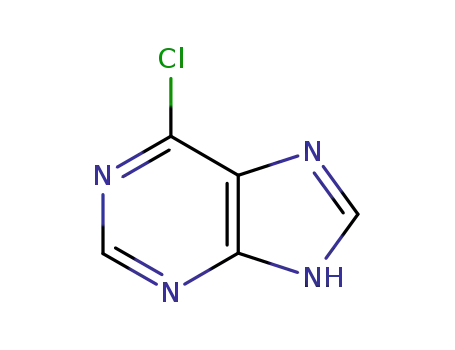
6-chloropurine
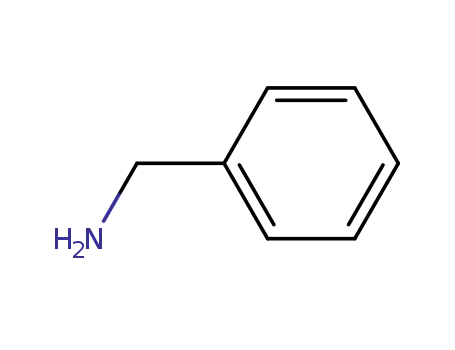
benzylamine

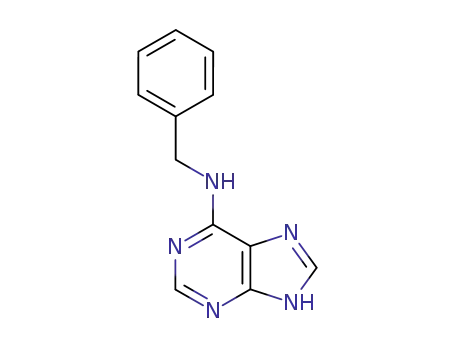
6-benzyladenine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
triethylamine;
In
ethanol;
for 5h;
Reflux;
|
96% |
|
at 100 ℃;
for 0.0833333h;
microwave irradiation;
|
95% |
|
With
indium(III) chloride;
In
acetonitrile;
at 120 ℃;
for 1h;
regioselective reaction;
Microwave irradiation;
|
93% |
|
In
water;
at 100 ℃;
for 0.75h;
Solvent;
Green chemistry;
|
92% |
|
With
triethylamine;
In
ethanol;
Reflux;
Inert atmosphere;
|
82% |
|
With
triethylamine;
In
butan-1-ol;
at 110 ℃;
for 3h;
|
69% |
|
With
N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 110 ℃;
for 0.25h;
Microwave irradiation;
|
61% |
|
With
N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine;
In
butan-1-ol;
Heating;
|
|
|
In
ethanol;
Reflux;
|
|
|
With
triethylamine;
In
ethanol;
at 80 ℃;
for 3h;
|
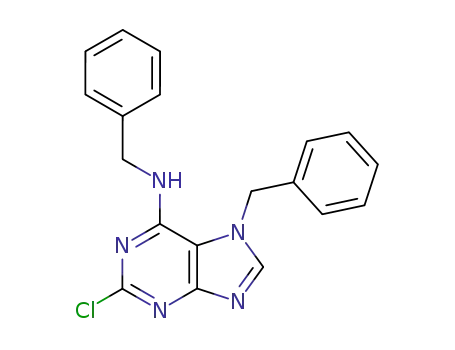
7-benzyl-6-benzylamino-2-chloropurine


6-benzyladenine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
potassium hydroxide; hydrogen;
palladium on activated charcoal;
In
ethanol;
for 15h;
under 760 Torr;
|
69% |
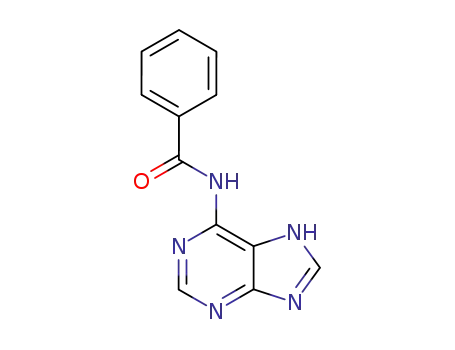
N6-benzoyladenine
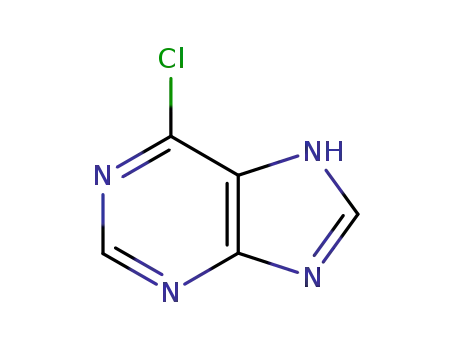
6-chloro-7H-purine
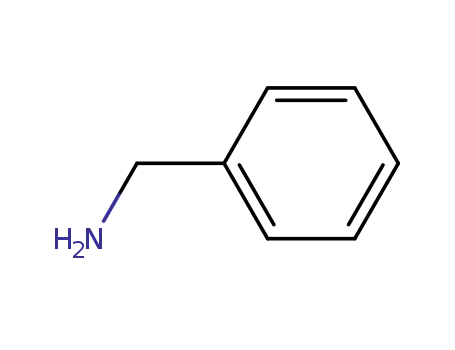
benzylamine
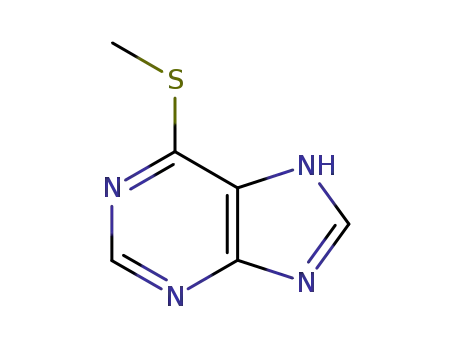
6-(methylthio)-1H-purine

3-(6-benzylamino-purin-9-yl)-butyric acid methyl ester
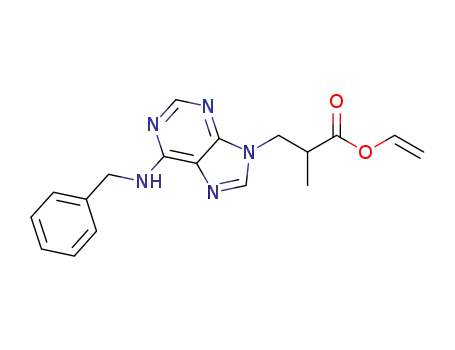
3-(6-benzylamino-purin-9-yl)-2-methyl-propionic acid vinyl ester
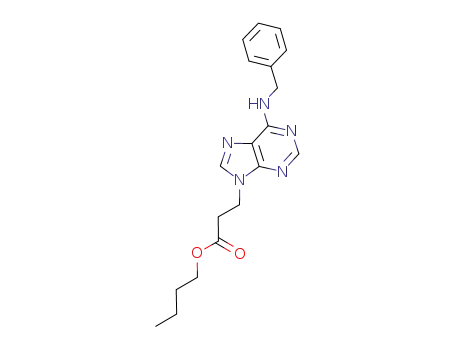
3-(6-benzylamino-purin-9-yl)-propionic acid butyl ester
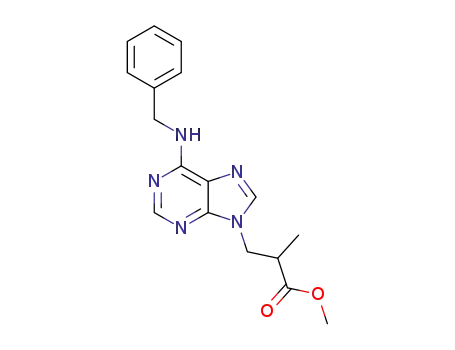
3-(6-benzylamino-purin-9-yl)-2-methyl-propionic acid methyl ester