Home > Products > intermediate
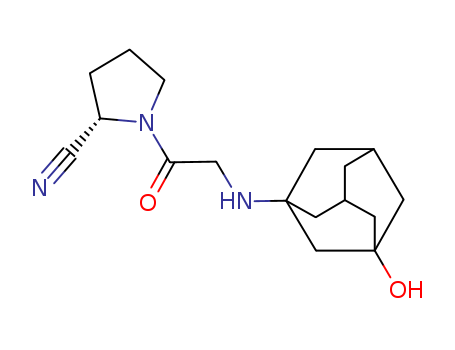







CasNo: 274901-16-5
MF: C17H25N3O2
Appearance: white crystalline powder
|
Indications and Usage |
Vildagliptin (vildagliptin), developed by Novartis (Novartis) Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, is another oral administrated inhibitor of Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV after sitagliptin (sitagliptin). In 2008, it is approved for marketing in the European Union for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease with its prevalence being increased year by year. Type 2 diabetes is a complicated diseases caused with the combined action between polygenic genetic factors and environmental factors. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitors are a new class of anti-diabetic drugs which induces and facilitate the biosynthesis and secretion of insulin. It plays a role in lowering the blood carbohydrate concentration through multiple mechanisms such as inhibiting the β cell apoptosis, inhibiting glucagon secretion and reducing food intake. During its lowering effect on reducing blood carbohydrate levels, it can also reverse the situation of deteriorating function of pancreas islet for diabetic patients at the same time. Vildagliptin is the representative of drugs among the dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitor. It exhibited a good anti-diabetic effects and tolerance no matter whether it is being administered alone or in combination with metformin and insulin medication in clinical studies. |
|
Mechanisms of Action |
Vildagliptin is a selective, competitive and reversible DPP-4 inhibitor. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide 21 (GLP21) are important hormones that regulate body glucose concentration and have the same functions as intestinal insulin. Type-2 diabetes patients suffer from GIP insulin secretion failure, so only their GLP21 can promote insulin secretion by affecting receptors on islet beta cell membranes. GLP21 can also inhibit glucagon secretion and inhibit gastric clearing to extend the feeling of fullness (control appetite). DPP-4 binds with proteins in many types of tissues, including tissue in the kidney, liver, small intestine brush border, pancreatic duct, lymph cells, and endothelial cells, and it can deactivate GLP21 by hydrolyzing its N-terminal position-2 alanine. Vildagliptin binds with DPP-4 to produce a DPP-4 compound and inhibit its activity. It increases GLP21 concentration and promotes islet beta cells to produce insulin, while also lowering glucagon concentration, thus lowering blood sugar. Vildagliptin has not noticeable effects on weight. |
|
Adverse reactions |
Most common adverse reactions include headache, nasopharyngitis, coughing, constipation, dizziness and excess sweating. There have been very rare cases of hypotension, but it is unclear if conditions are related to this drug. Almost all research shows that the hypoglycemia occurrence rate while using Vildagliptin is similar to the rate when using a placebo. Control trials showed that compared to thiazolidinediones, Vildagliptin causes a similar occurrence rate of headaches, rashes, and other adverse reactions, but Vildagliptin has a lower occurrence rate of adverse reactions forcing patients to cease treatment and of severe adverse reactions. |
|
Side effects |
The most common adverse events reported in patients receiving vildagliptin included headache, nasopharyngitis, cough, constipation, dizziness, and increased sweating. Vildagliptin is not recommended for patients with liver impairment. |
|
Synthesis |
Vildagliptin is chemically derived in three steps starting from L-prolinamide via acylation with chloroacetyl chloride to produce 1-(chloroacetyl)-L-prolinamide, subsequent dehydration of the carboxamide group to the nitrile with trifluoroacetic anhydride, and condensation of the 1-(chloroacetyl)-L-prolinenitrile intermediate with 3-hydroxyadamantan-1-amine. |
|
Drug interactions |
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs None known |
|
Metabolism |
About 69% of a dose of vildagliptin is metabolised, mainly by hydrolysis in the kidney to inactive metabolites. About 85% of a dose is excreted in the urine (23% as unchanged drug), and 15% in the faeces. |
|
Brand name |
Galvus |
InChI:InChI=1/C18H17F6N3O.H3O4P/c19-13-8-15(21)14(20)6-10(13)5-11(25)7-17(28)26-3-4-27-12(9-26)1-2-16(27)18(22,23)24;1-5(2,3)4/h1-2,6,8,11H,3-5,7,9,25H2;(H3,1,2,3,4)/t11-;/m1./s1
An efficient and high-yielding synthetic...
The present invention relates to process...
The invention discloses a continuous pre...
The invention discloses a synthesis meth...
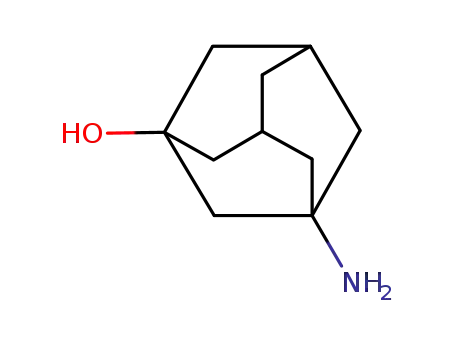
3-aminoadamantan-1-ol

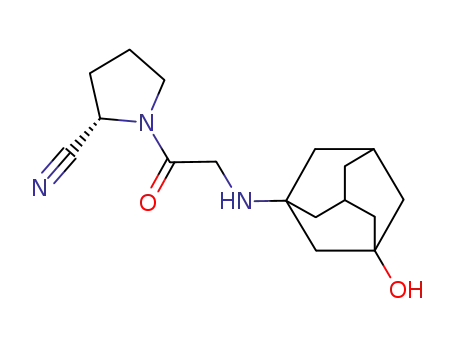
vildagliptin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
potassium carbonate; potassium iodide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 40 ℃;
for 3h;
Reflux;
|
82% |
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1: potassium carbonate; potassium iodide / tetrahydrofuran / 5 h / Reflux
2: potassium hydroxide; water / 12 h / 20 °C
3: dmap; dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide / dichloromethane / 6 h / 20 °C
With
dmap; water; potassium carbonate; dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide; potassium iodide; potassium hydroxide;
In
tetrahydrofuran; dichloromethane;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1: tetrahydrofuran / 3 h / Reflux
2: sodium tetrahydroborate; methanol / 0.5 h
3: dmap; dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide / dichloromethane / 6 h / 20 °C
With
methanol; dmap; sodium tetrahydroborate; dicyclohexyl-carbodiimide;
In
tetrahydrofuran; dichloromethane;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 5 steps
1: water / 48 h / 20 - 30 °C
2: triethylamine; 2,4,6-tripropyl-1,3,5,2,4,6-trioxatriphosphinane-2,4,6-trioxide / acetonitrile / 3 h / 20 - 30 °C / Inert atmosphere
3: triethylamine / dichloromethane / 5 h / 0 - 10 °C / Inert atmosphere
4: potassium carbonate; methanol / 4 h / 40 °C
5: hydrogenchloride / water / 7 h / 70 °C
With
hydrogenchloride; methanol; potassium carbonate; 2,4,6-tripropyl-1,3,5,2,4,6-trioxatriphosphinane-2,4,6-trioxide; triethylamine;
In
dichloromethane; water; acetonitrile;
|
|
|
With
potassium carbonate; potassium iodide;
In
acetone;
at 25 - 30 ℃;
Reagent/catalyst;
Solvent;
Time;
Temperature;
|
56.5 g |
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1.1: potassium carbonate; potassium iodide / dichloromethane / 0.5 h / Reflux; Inert atmosphere
1.2: 6 h / Reflux
2.1: ammonia / methanol / 10 - 75 °C
3.1: trifluoroacetic anhydride; trifluoroacetic acid / 2-methyltetrahydrofuran / Reflux
3.2: 5 - 10 °C
With
ammonia; potassium carbonate; trifluoroacetic acid; trifluoroacetic anhydride; potassium iodide;
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran; methanol; dichloromethane;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 4 steps
1.1: potassium carbonate; potassium iodide / ethyl acetate / 75 °C
2.1: sodium hydroxide; water / 65 - 70 °C
3.1: 2,4,6-tripropyl-1,3,5,2,4,6-trioxatriphosphinane-2,4,6-trioxide; N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine / ethyl acetate; acetone
4.1: trifluoroacetic anhydride; trifluoroacetic acid / 2-methyltetrahydrofuran / Reflux
4.2: 5 - 10 °C
With
water; potassium carbonate; 2,4,6-tripropyl-1,3,5,2,4,6-trioxatriphosphinane-2,4,6-trioxide; N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine; trifluoroacetic acid; trifluoroacetic anhydride; potassium iodide; sodium hydroxide;
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran; ethyl acetate; acetone;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 5 steps
1.1: potassium carbonate; potassium iodide / ethyl acetate / 75 °C
2.1: sodium hydroxide; water / 65 - 70 °C
3.1: triethylamine / dichloromethane / 0.5 h
3.2: 0.5 h
4.1: ammonia / methanol / 10 - 75 °C
5.1: trifluoroacetic anhydride; trifluoroacetic acid / 2-methyltetrahydrofuran / Reflux
5.2: 5 - 10 °C
With
ammonia; water; potassium carbonate; triethylamine; trifluoroacetic acid; trifluoroacetic anhydride; potassium iodide; sodium hydroxide;
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran; methanol; dichloromethane; ethyl acetate;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 5 steps
1.1: methanol / 10 h / Inert atmosphere; Reflux
1.2: 0 - 25 °C
2.1: potassium carbonate; potassium iodide; tetrabutylammomium bromide / N,N-dimethyl-formamide / 10 h / 80 °C / Inert atmosphere
3.1: ammonia / methanol / 70 °C
4.1: trifluoroacetic anhydride / 2-methyltetrahydrofuran / Inert atmosphere
5.1: palladium 10% on activated carbon; hydrogen / methanol / 22 h
With
palladium 10% on activated carbon; tetrabutylammomium bromide; ammonia; hydrogen; potassium carbonate; trifluoroacetic anhydride; potassium iodide;
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran; methanol; N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 6 steps
1.1: methanol / 10 h / Inert atmosphere; Reflux
1.2: 0 - 25 °C
2.1: potassium carbonate / N,N-dimethyl-formamide / 20 °C
3.1: sodium hydroxide; water / methanol / 2 h / 65 °C
4.1: triethylamine; 2,4,6-tripropyl-1,3,5,2,4,6-trioxatriphosphinane-2,4,6-trioxide / N,N-dimethyl-formamide; ethyl acetate / 2 h / 25 °C / Inert atmosphere
5.1: trifluoroacetic anhydride / 2-methyltetrahydrofuran / Inert atmosphere
6.1: palladium 10% on activated carbon; hydrogen / methanol / 22 h
With
palladium 10% on activated carbon; water; hydrogen; potassium carbonate; 2,4,6-tripropyl-1,3,5,2,4,6-trioxatriphosphinane-2,4,6-trioxide; triethylamine; trifluoroacetic anhydride; sodium hydroxide;
In
2-methyltetrahydrofuran; methanol; ethyl acetate; N,N-dimethyl-formamide;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 6 steps
1.1: methanol / 10 h / Inert atmosphere; Reflux
1.2: 0 - 25 °C
2.1: potassium carbonate; potassium iodide; tetrabutylammomium bromide / N,N-dimethyl-formamide / 10 h / 80 °C / Inert atmosphere
3.1: triethylamine / toluene / 110 °C / Inert atmosphere
4.1: ammonia / methanol / 70 °C
5.1: triethylamine; trichlorophosphate / 2 h / 10 - 40 °C
6.1: hydrogenchloride / water / 15 - 25 °C
With
hydrogenchloride; tetrabutylammomium bromide; ammonia; potassium carbonate; triethylamine; potassium iodide; trichlorophosphate;
In
methanol; water; N,N-dimethyl-formamide; toluene;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1.1: methanol / 3 h / Reflux
1.2: 0 - 5 °C
2.1: sodium carbonate; sodium iodide / acetonitrile / 6 h / Inert atmosphere; Reflux
3.1: palladium 10% on activated carbon; hydrogen / methanol / 20 °C
With
palladium 10% on activated carbon; hydrogen; sodium carbonate; sodium iodide;
In
methanol; acetonitrile;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1.1: potassium carbonate / dichloromethane / 2 h / -5 °C
2.1: potassium hydroxide; ethanol / 65 °C
3.1: sodium hydroxide / dichloromethane / 1.5 h / 0 °C
3.2: 0 °C
With
ethanol; potassium carbonate; potassium hydroxide; sodium hydroxide;
In
dichloromethane;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1: N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine; acetic anhydride / tetrahydrofuran / 2 h / Reflux
2: tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) borate / toluene / 12 h / Inert atmosphere; Reflux
3: ammonium formate; palladium on activated charcoal / tetrahydrofuran / 8 h / 20 °C
With
tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) borate; palladium on activated charcoal; ammonium formate; acetic anhydride; N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine;
In
tetrahydrofuran; toluene;
|
|
|
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1: N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine; acetic anhydride / tetrahydrofuran / 2 h / Reflux
2: tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) borate / toluene; water / 12 h / Inert atmosphere; Reflux
3: palladium on activated charcoal; ammonium formate / tetrahydrofuran / 10 h / 20 °C
With
tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) borate; palladium on activated charcoal; ammonium formate; acetic anhydride; N-ethyl-N,N-diisopropylamine;
In
tetrahydrofuran; water; toluene;
|
![(2S)‐1‐[[(3-hydroxytricyclo[3.3.1.1[3,7]]decane-1-yl)imino]acetyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile](/upload/2025/4/a7da33a5-fb6e-4835-8266-8f931ab9daae.png)
(2S)‐1‐[[(3-hydroxytricyclo[3.3.1.1[3,7]]decane-1-yl)imino]acetyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile


vildagliptin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
palladium on activated charcoal; ammonium formate;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 8h;
Reagent/catalyst;
Solvent;
Temperature;
|
91.9% |
|
With
palladium on activated charcoal; ammonium formate;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 20 ℃;
for 10h;
Solvent;
Reagent/catalyst;
Temperature;
|
91.9% |

3-aminoadamantan-1-ol
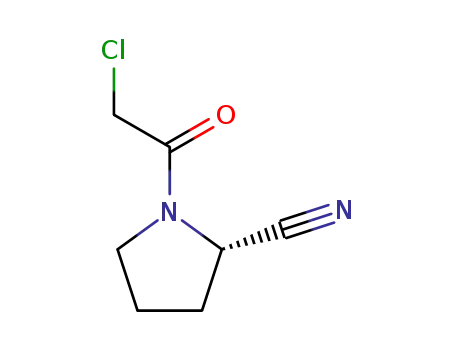
(S)-1-(2-chloroacetyl)pyrrolidine-2-carbonitrile
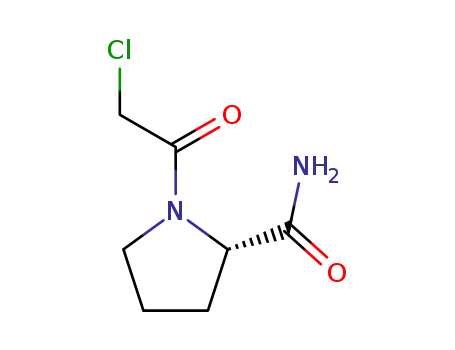
(S)-1-(2-chloroacetyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
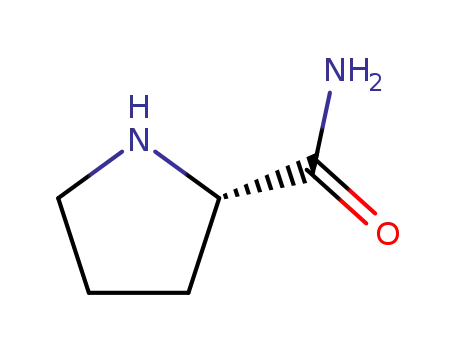
L-prolinamide
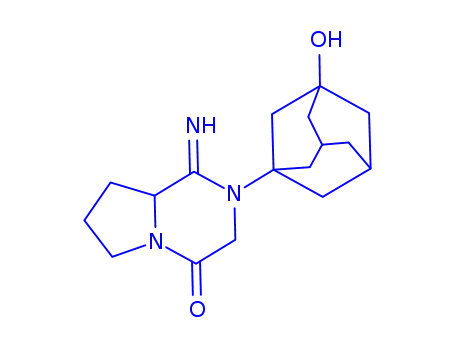
2-(3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)-1-imino-hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazin-4-one
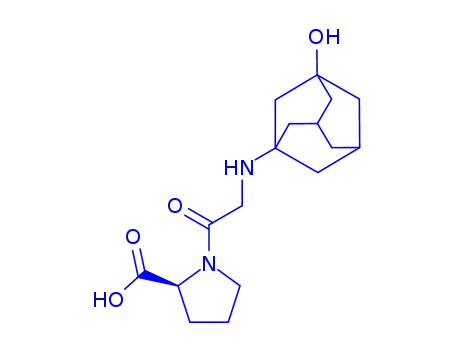
vildagliptin carboxylic acid